Intune operations par excellence
Introduction
Im my daily work as engineer and consultant I accompany organizations from several industries on their way to modern endpoint management with Microsoft Intune. Beside the technical challenges, I often see that some topics get a little less attention and remain unclear. This is dangerous, because this can affect a whole initiative negatively so that stakeholders and/or users are unsatisfied with the new technology. To successfully deliver an endpoint platform that enables end users to get more productive than they ever have been; the technical, organizational and operational parts must be innovated. Though, innovation is a broad term. I like to define it as "rethink your IT from a technical, process and security angle and align it to your future IT strategy and Microsoft's strategy". The importance of effective operations with Intune and technologies around it, is not to be underestimated - even though they will bring benefits to the audience, namely the end user and IT department. In the end, for the organization it is all about reduction of effort, time, money and resources.
This collection names some of the usual suspects which I encounter often. If you already master these; congrats your platform seems to be delivered with excellence 🚀
- RBAC
- Device type and policy list (use cases)
- User and group list
- App inventory
- Device & asset management including lifecycle
- Minimum compliance policy requirements
- Monitoring (engineering part)
- Change management
- Piloting new features
- Feedback loop
- Vendor/OEM strategy
- Support of end user
- Technology changes
In the following chapters, I will cover these topics.
Role-based access control
Intune role-based access control allows administrators to control the level of access to the Intune portal and its resources. Define a concept of Intune operations in the portal and have clear responsibilities. Some of the key takeaways from the linked blog posts below:
- Understand Intune and Entra roles
- Assess currently assigned roles
- Write a concept on job roles/people and their responsibilities and access level
- Consider governance concepts in Intune
- Understand RBAC areas for devices
- Design a solution concept to special access for certain use cases

Device type and policy list (use cases)
Your Intune tenant hosts your profiles, devices and resources. Please document the use cases e.g. standard device, Kiosk, Windows 365 clearly and have a list of which profiles and apps are assigned to which device types. This could look alike:
| Type 1 - standard device | Type 2 - Kiosk | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Standard workers device for daily work with core apps. | Dedicated devices for Kiosk mode. |
| Entra ID group | sg-AllAutopilotDevices | sg-AllKioskDevices |
| Join type | Entra Join | Entra Join |
| Deployment Profile | Entra Join User deploy | Entra Self-deploy |
| Compliance Profile | Windows-COPE-Compliance-Default | Windows-COPE-Compliance-Reduced |
| Configuration Profiles | Windows-COPE-SettingsCatalog-Windows, Windows-COPE-SettingsCatalog-Edge | Windows-COPE-SettingsCatalog-Kiosk |
| Endpoint Security | Windows-COPE-EndpointSecurity-DefenderAV | Windows-COPE-EndpointSecurity-LAPS |
User and group list
The same list approach applies to users and groups. Because most environments will differentiate from certain user groups (department, job roles, sub-organization, country etc.). Most importantly, the identity side including lifecycle and attributes must be well cared of. Here, it is definitely recommended to work with Entra dynamic groups.
App inventory
An app inventory is another list, that provides an overview on the applications which are deployed through Intune. This is particularly helpful when you have a lot of applications or multiple use cases for device types. For a minimum, I would structure it as following:
| Name | Source/type | License | Assignment Required | Assignment Available | Assignment Uninstall | App owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company Portal | Store | - | All devices | Intune team | ||
| Business app | win32 | Yes | All devices | Business team |
Device & asset management including lifecycle
Intune is not an asset management product, keep that in mind. You should have an external system that stores information to all of your assets. Only through adhering a clear concept, the lifecycle can be good maintained. There are several reasons and inputs, when it comes to this:
- If the Autopilot hash is deleted from your tenant, you will lose track of the device
- If a hardware replacement takes place, the device will be reset and potentially receives a new mainboard with new hash
- Every device that is decomissioned should be deleted from the tenant, otherwise the device allows and forces to sign-in with a corporate account (security vulnerability and undesired behavior)
- Intune can clean up devices after a period of time when the device does not check in
- Intune provides a primary user, but unfortunately not very much more attributes > think about device ownership, device physical location, custom attributes and the whole accounting part

Monitoring (engineering part)
Once your Intune deployment is complete, do not forget to monitor it! It is a living system and part of your security posture.
- Proactively look into the reports and monitoring
- Intune built-in reports
- Defender for Endpoint
- Windows Update for Business reports
- Log forwarding to Log Analytics Workspace
- 3rd party products
-> and take action!
- Oversee the service health
- Check your tenant connectors
- Review your inventory and remove obsolete items/content
- Stale devices (don't forget from the Entra ID side too)
- Outdated or unused apps
- Profiles that are not productive
Change management
Track your changes and have governance controls! This is key for a successful operation, do not just make changes to the environment. All is applied instantly and you better know what the changes were in the past if something unexpected comes up. Best practice would be that you already have a change management system in the organization or you start your own one with just a list.
Take a look at my community tool:

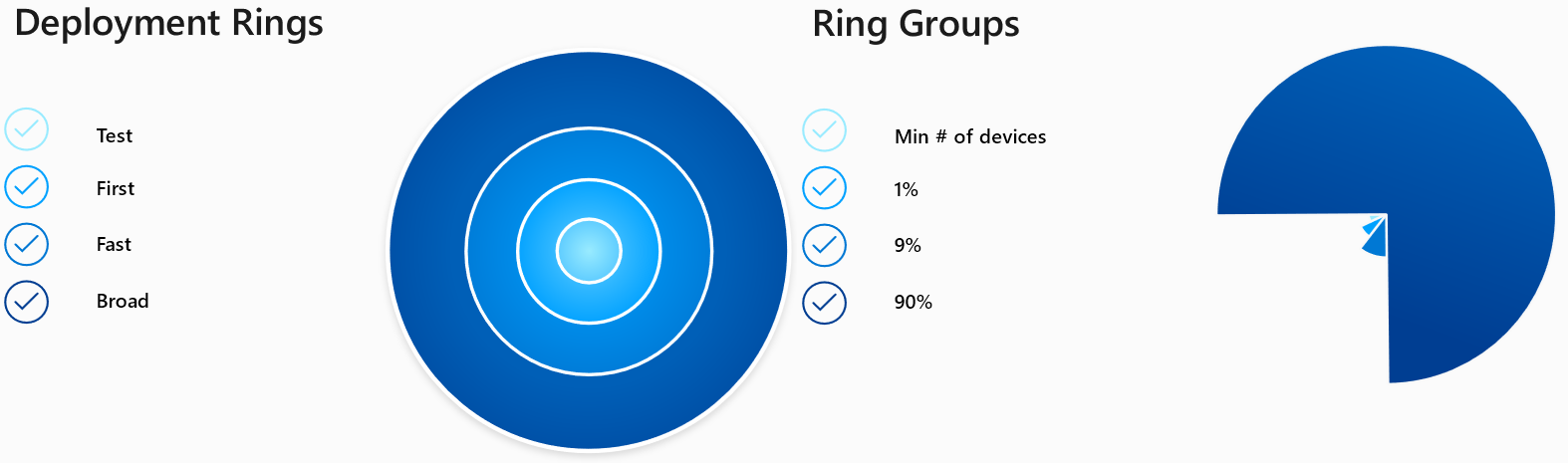
Piloting new features
Testing and piloting of new features is needed, because it ensures the quality throughout the technology and safeguards you from user complaints afterwards. With that said, every single new feature or change should have a process included to test it. (Including change management) For instance, define pilot users that always get the latest features but are aware that some thing might go wrong. Orientate with deployment rings:
Feedback loop
It only makes sense to collect feedback when piloting new features. Without that, there is a risk that technology and the business are not aligned. This negatively impacts the end user satisfaction and trust to the IT. "Feedbackers" may be:
- Stakeholders
- Pilot users
- Users near to the IT department and non-mission critical
Consider release management processes and raise awareness that sometimes things go wrong.
Vendor/OEM strategy
We may not forget about the hardware, that continously must be renewed due to technology development. A vendor or original equipment manufacturer can provide hardware and be aware that they can also relief you from effort. Things to clarify:
- Vendor strategy
- Single- or multi-vendor
- Latest devices of series XYZ
- Ordering process
- Consider vendor specific services (e.g. cloud recovery)
- Ordering process
- Upload hardware hash to tenant
- UEFI settings
- OS
- Latest Windows built in Pro edition
- Remove bloatware
- Language and locale en-us
- Lifecycle (hardware)
Compliance policy requirements
Enforcing compliance requirments might be a one-time task through applying policies. Nevertheless, requirements are likely to change over time and must be technically reflected. Involving the end users is key because this is no other thing as a change (management) process. So communication between IT and the rest of the org is a real success factor.
Support of end user
A technology is only as good as the end users make it. And that includes that they receive support from professionals who know it and are responsible for. Regarding troubleshooting around Intune, I recommend you to read this posts:


Technology changes
Microsoft Intune is a cloud SaaS, which means that Microsoft can release updates and bring innovation at any time. Think about how your organization can profit or how you can enable individuals even more. With that said, learning is the most important part!
Good sources are:
- Community blogs
- Microsoft officials
- Message Center
Stay up to date and align your technology strategy!
Read more on Intune: