Intune compliance intro
Introduction
Most organizations have compliance requirements for dozens of topics, spanning both technical and non-technical domains, as they are in a complex landscape of regulations, standards, and best practices to ensure the integrity, security, and conduct of their operations.
This post is just picking one technical subject out of it, which is related to Microsoft Intune 😉
What device compliance means
Before we can talk about device compliance, we need to open up the discussion on the "why" device compliance is important. Devices are:
- Corporate assets
- Access platform for organizational data
- The stage for professional work
- Interaction point of end user
As you see, devices are quite an important good and therefore need to follow compliance principles. From a technical view, we need to enforce settings and validate them. Important to know:
- Configuration profiles or any other feature set
- Compliance policies validate of what is set (they are read-only on the system)
Compliance in Intune
In Intune it is possible to create compliance policies for any OS that can be assigned to users or devices. They hold multiple configuration settings and rules of these scopes:
- Custom Compliance - create own script that discovers settings
- Device Health - Windows Health Attestation / Windows 11 Device health attestation
- Device Properties - OS version and build
- Configuration Manager Compliance - signals from SCCM in co-management scenario
- System Security - Password, Encryption, Defender related settings
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint - Integration to include machine risk score
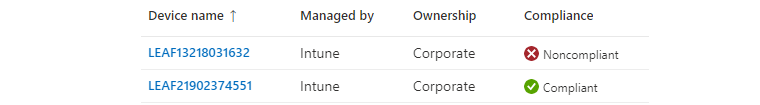
Once they evaluated the status on the device, the status of compliant or not compliant is reported back to Intune.
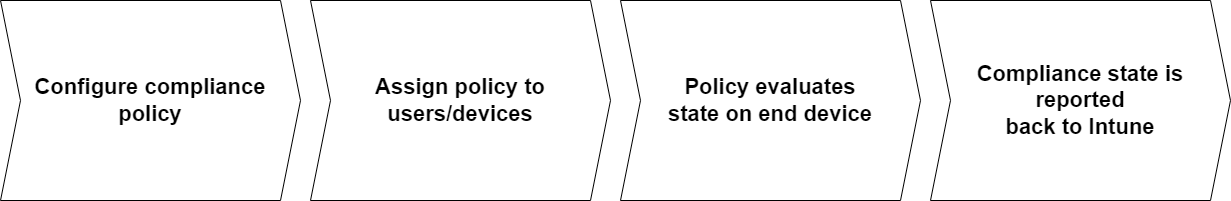
What to do with device compliance?
We now understand the significance of compliance and how it integrates with Intune. So far, it's just showing us a signal and the current status, without doing anything else.
To use that signal to control something, we need to bring in another component: Conditional Access. See the architecture below:
Eventhough the compliance state can be used to allow access to resources, don't forget about Zero Trust.
Components
Required:
- Intune compliance policy
- Conditional Access
Optional signal sources:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- ConfigMgr
Device compliance architecture
Take a look at the architecture and flows when devices are evaluated for compliance.
- Intune applies and receives settings regarding compliance
- The device compliance state can be used as a "grant control" in Conditional Access along with other signals
- If prerequisites are met, Defender for Endpoint forwards a signal of machine risk score to Intune
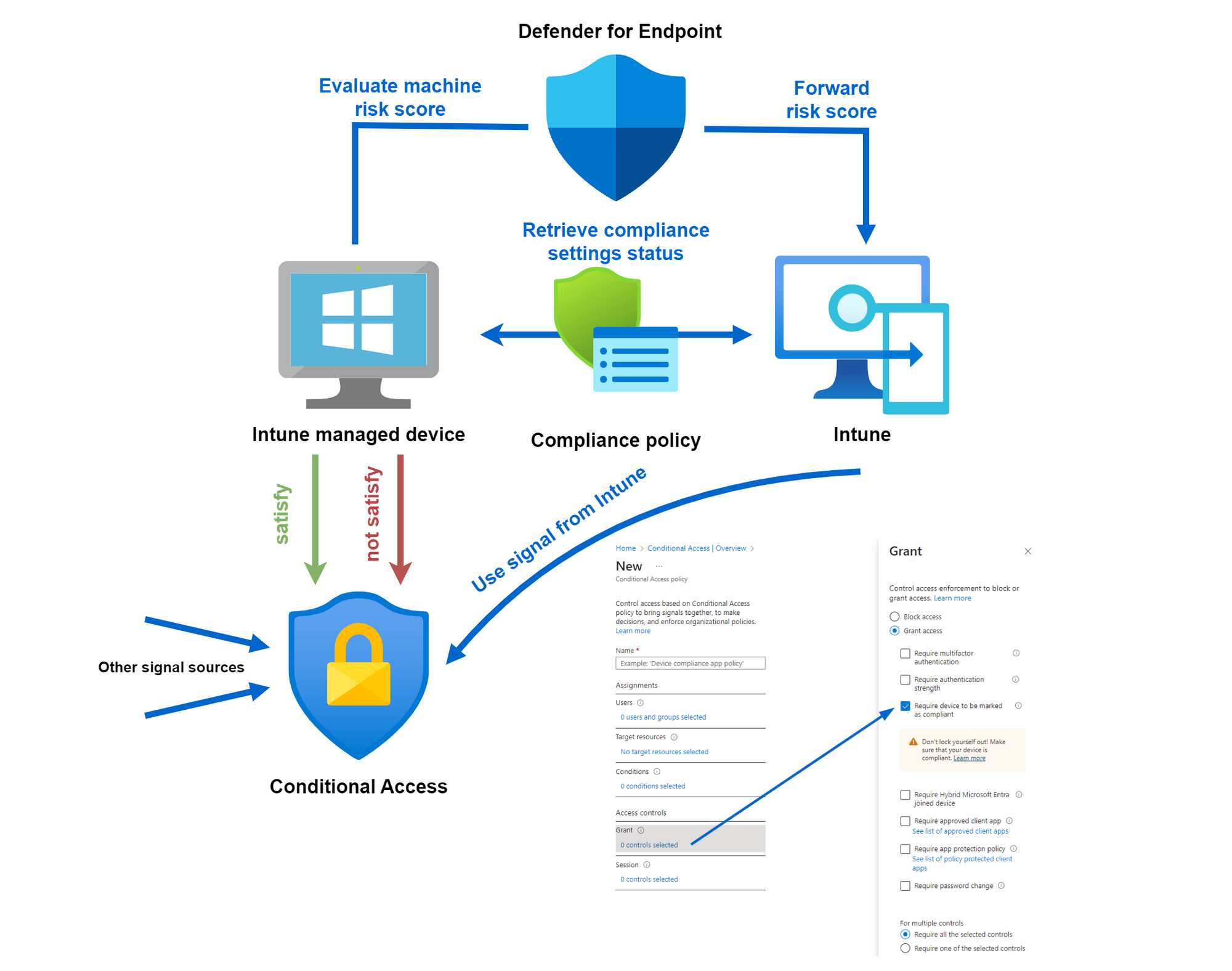
Conditional Access
In combination with Conditional Access, device compliance can be used as a very powerful signal. "Require device to be marked as compliant" is the grant control, that correlates to the signal from Intune.
There are some common use cases to leverage the signal of a compliant device:
- To register or modify personal security information
- To access sensible applications
- Establish Global Secure Access connection (preview)
Requirements:
- Device is Entra ID registered
- Device is Intune enrolled (to apply the policy)
- Supported on Windows 10+, iOS, Android and macOS
- Edge InPrivate mode is considered as "not compliant"
Device compliance policy for Windows
The following table shows my universal applicable and recommended settings in a compliance policy.
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BitLocker | Require | Encryption |
| Secure Boot | Require | Verify integrity before booting |
| Code integrity | Require | Verify integrity of system files |
| Minimum OS version | Latest OS version | OS minimum requirement, please note to continuously rise |
| Firewall | Require | Control network connections |
| Trusted Platform Module (TPM) | Require | Security chip on device |
| Antivirus | Require | System protection |
| Antispyware | Require | System protection against spyware |
| Microsoft Defender Antimalware | Require | System protection against malware |
| Microsoft Defender Antimalware security intelligence up-to-date | Require | Antimalware data up-to-date |
| Real-time protection | Require | Real-time system protection |
| Require the device to be at or under the machine risk score | Medium | Signal from MDE to consider machine risk score |

Actions for noncompliance
Next you can configure what happens if a device is not fulfilling the settings from before.
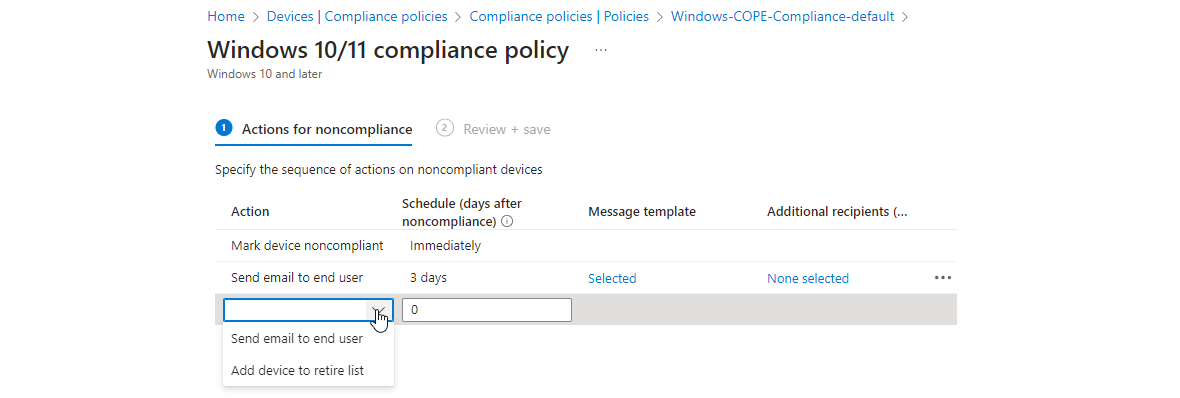
It makes sense to create custom message templates/notifications. It depends from organization and workload how these should look and after how many days the user should receive such a mail.
Tenant compliance settings
Don't forget about the tenant-level compliance settings found at: Intune admin center>Devices>Compliance>Compliance policy settings
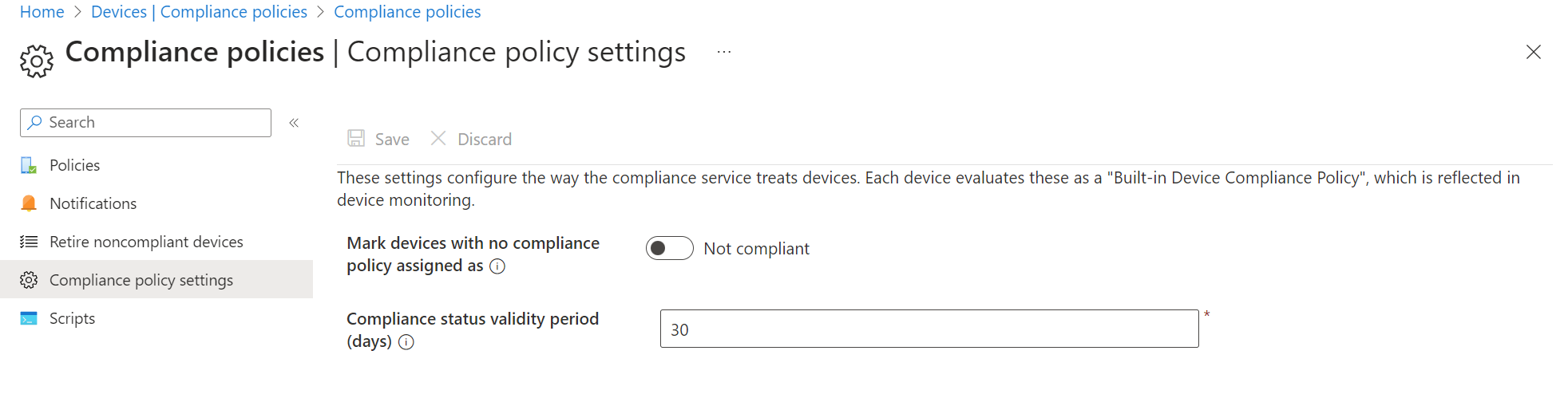
| Setting | Recommended value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mark devices with no compliance policy assigned as | Not compliant | When a device has no compliance policy assigned, which compliance state it should get |
| Compliance status validity period (days) | 7 | Period of time in which the device must report the compliance settings status before it is considered as non compliant |
Deployment plan
Just a quick and dirty deployment plan from the field:
- Define your scope
- Target users and devices (managed/unmanaged)
- Target OS
- Required compliance settings
- Define Conditional Access integration
- Configure settings and create Conditional Access policy
- Assign on test group and pilot
- Inform end users
- Roll out (enable policy for all)
Conclusion
Organizations utilizing Intune should leverage its ability to enforce device compliance through profiles. In the Microsoft ecosystem, this signal can be seamlessly incorporated into Conditional Access, making it an important indicator. However, when implementing such controls, thorough testing and a staged rollout process are essential. Implementing at least a read-only policy can be beneficial. It's crucial to bear in mind that non-compliant devices may lose access to organizational data and apps in certain scenario. As a result, continuous monitoring of device compliance status is needed by an IT admin.
Want more? Read my post on Intune compliance: tips from the field




